In recent news, a private company has successfully launched the largest rocket ever built by the human race into space. This monumental achievement marks a significant milestone in the field of space exploration and demonstrates the capabilities of private companies in pushing the boundaries of space technology.
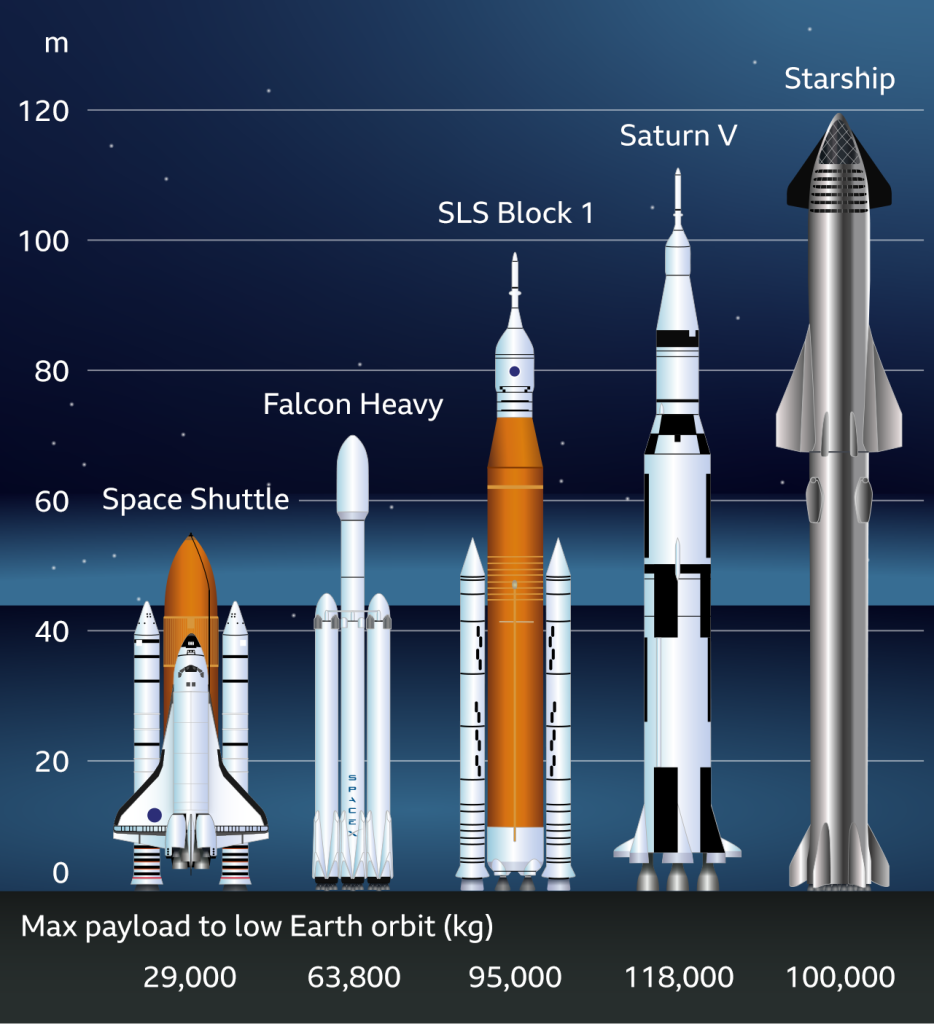
The rocket responsible for this historic launch is called Starship, developed by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk. Starship is a two-part rocket system consisting of the Super Heavy booster as its first stage and the Starship upper stage. Together, they form the largest rocket ever built.
Here are some key details about the Starship rocket:
Size and Power:
The Super Heavy booster stands an impressive 70 meters (230 ft.) tall and is powered by 33 engines, producing over 7.6 million kg (16.7 million lbs) of thrust.
The Starship upper stage stands 50 meters (164 ft.) tall and is equipped with six of the same 33 engines used in the first stage.
The overall stack, made entirely of stainless steel, reaches a height of 40 stories.
Purpose and Potential:
Starship has been designed to serve various purposes, including space tourism, NASA’s Artemis program, and potential human settlement on Mars.
It has been selected by NASA as the Human Landing System (HLS) for the Artemis program, which aims to return astronauts to the lunar surface.
The upper stage of Starship could potentially carry up to 100 passengers, making it a significant player in future space missions.
Recent Launch:
The recent launch of Starship was its second-ever test flight, which took place on November 18.
While the launch successfully took the Starship upper stage to space for the first time, the Super Heavy booster experienced an explosion shortly after stage separation.
SpaceX referred to the event as a “rapid unscheduled disassembly” and stated that the automated flight termination system on the second stage triggered late in the burn.
This successful launch of the largest rocket ever built by a private company showcases the progress and ambition of private space exploration initiatives. It highlights the potential for future advancements in space technology and the role of private companies in shaping the future of human spaceflight.

